Whether seeking better posture, lesser back pain, or a physique to be proud of, strengthening your back muscles is a pursuit worth considering. After all, our back plays a crucial role in our everyday movements and stability. However, to approach this effectively, it’s important that you comprehend the structure and function of the different back muscles – from the latissimus dorsi to the erector spinae. Additionally, mastering strength training exercises, such as deadlifts or pull-ups, can enhance your back strength, along with the appropriate incorporation of cardio into your routine. Let’s not forget the power of flexibility and rest in muscle recovery and growth, nor the role of nutrition in developing muscle strength. Setting out on the journey to a stronger back can be a lot to take in, but with the right knowledge and understanding, the path becomes clearer.
Understanding Back Muscles
Understanding Back Muscles: An Overview
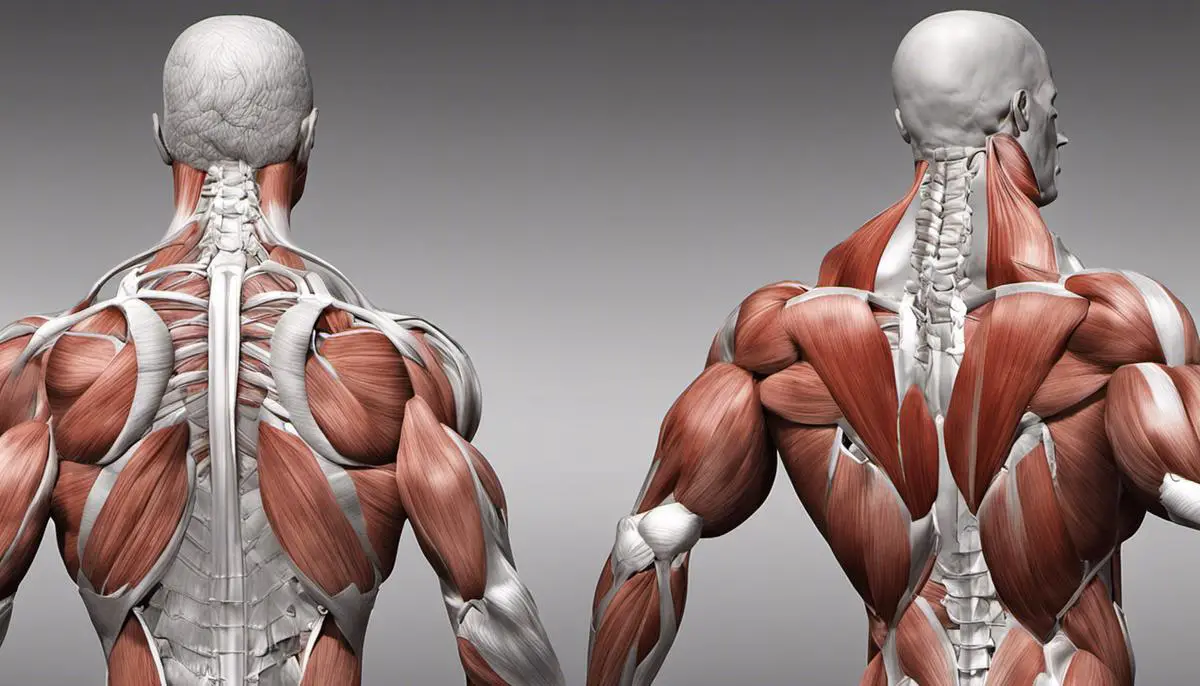
Your back has several major muscle groups that are essential for a wide range of daily functions, and strengthening them can lead to improved posture, flexibility, and reduced risk of injury. These major muscle groups include the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, rhomboids, and erector spinae.
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi — often simply called “the lats” — are large muscles in the lower and middle part of the back. They’re responsible for the movement and stability of the arms in relation to the spine. When you pull something down or towards your body, you’re using your latissimus dorsi. Strengthening these muscles can lead to better overall upper body strength.
Trapezius
The trapezius, or “traps”, are the muscles located between your shoulders and neck. They control the tilting and turning movements of your neck and head, and also help in moving and stabilizing your shoulder blades. Exercising this muscle can help you maintain proper posture and reduce the risk of neck strain.
Rhomboids
The rhomboids are smaller muscles situated underneath your trapezius. Although they aren’t as large as other back muscles, they play a crucial role in the retraction of the shoulder blades — when you pull your shoulder blades back and down, that’s your rhomboids at work. Strengthening these muscles can help improve posture and prevent shoulder-related injuries.
Erector Spinae
Last, but certainly not least, the erector spinae are a group of muscles and tendons running along the spine. They’re responsible for keeping your spine straight and assisting with side-to-side movements. Strengthening the erector spinae can be beneficial in maintaining spinal health and avoiding lower back pain.
Remember, understanding your back and its complex muscle structure can help you to focus more on your targets and perform strength-building exercises safely and effectively. Consider working with a physical trainer or a sports medicine professional for personalized advice based on your fitness goals and physical condition.

Strength Training Exercises
Deadlifts: A Compound Movement for Back Strength
The deadlift is a compound exercise that targets the entire back, engaging muscles in the lower, middle, and upper regions. To perform a deadlift, stand with your feet hip-width apart and bend at the hips and knees to reach the bar. Grip the bar with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart and extinguish any slack in the bar. Lift the bar by driving your hips forwards and keeping your chest up and back straight. Lower the bar by reversing the motion. Include deadlifts in your training regimen for a stronger back. Typically, perform 3 sets of 6 to 8 reps to build strength.
Bent-over Rows: Activation of Key Back Muscles
Bent-over rows target the latissimus dorsi (lats), traps, and the rhomboids in your back. To perform this exercise, hold a barbell or two dumbbells with an overhand grip. Bend your knees slightly and lean forward from your waist, keeping your back straight. Pull the weight up to your chest, keeping your elbows close to your body. Lower the weight, fully extending your arms. Start with 2 or 3 sets of 10 to 12 repetitions.
Pull-ups: The Backbone of the Back Training Regimen
Pull-ups are a powerful exercise targeting your back muscles, particularly the lats. Grip the bar with your palms facing away from your body, and pull yourself up until your chin is above the bar. Avoid swinging and use a controlled movement. Use a negative (slow descent) technique if you cannot perform full pull-ups yet. Aim for 4 sets of as many reps as you can safely do with good form.
Lat Pulldowns: Isolation Work for the Lats
Lat pulldowns are made for strengthening the latissimus dorsi (lats) muscle. Sit at a lat pulldown station, grip the bar with your palms facing forward, and pull the bar down to the top of your chest. Slowly let the bar rise back to the starting position. These are great for isolation and should be performed in 3 sets of 10 to 12 reps.
In strength training exercises such as these, remember to safely perform each movement, start with manageable weights, and gradually increase as your strength builds. Proper form is crucial to targeting the correct muscles and avoiding injury. Training regularly and consistently will yield the best results for a stronger back.

Incorporating Cardio into your Routine
Understanding the Importance of Cardio Exercises for Back Strength
Cardio exercises are pivotal to enhancing back strength and promoting overall fitness. Cardio workout like swimming, rowing, or even high-intensity interval training, known as HIIT, burn calories, reduce body fat, and strengthen the muscles in your back. With these exercises, you don’t just get a healthier heart, but also a stronger back.
How Cardio Complements Strength Exercises
Cardio and strength training are two different disciplines, but they deeply complement each other. Strength training is designed to build and strengthen muscles. Meanwhile, cardio, or aerobic exercise, strengthens your cardiovascular system, which includes your heart, lungs, and blood vessels. Integrating cardio into your routine helps elevate your heart rate and improves your heart’s fitness, which can be beneficial during strength training exercises where your cardiovascular system is working hard to supply your muscles with the oxygen they need.
The Role of Cardio in Muscle Recovery
It’s also essential to understand how cardio aids in muscle recovery. After a vigorous strength training session, your muscles need time to recover. Including low-impact cardio sessions in your routine can speed up this process. These exercises improve blood flow to the muscles, supplying them with oxygen and nutrients needed for recovery. Moreover, improved circulation may help flush out waste products, like lactic acid, that can build up during strenuous strength training. This kind of active recovery can help prevent muscle stiffness and soreness.
Incorporating Cardio into Your Strength Training Routine
To build a stronger back, you can engage in cardio exercises like swimming or rowing that inherently work out your back muscles. For instance, swimming strokes like the freestyle and backstroke use a wide range of muscles including those in the back, thereby strengthening them over time. Similarly, rowing is an excellent full-body workout that mainly targets your back muscles, promoting strength and endurance.
HIIT Workouts for Back Strength
Consider adding high-intensity interval training (HIIT) sessions to your routine. HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by short periods of rest or lower intensity exercise. This powerful form of cardio workout engages several muscle groups, including your back, and can result in improved muscle tone and strength.
Remember to start slow and progressively increase the intensity of your workouts. Additionally, always ensure your form is correct to avoid injuries. It’s also advisable to consult with a fitness professional or physical therapist to establish the most effective and safe exercise regimen for your needs and fitness level.

Importance of Flexibility and Rest
The Importance of Flexibility in Building Back Muscle
Muscular flexibility plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy and strong back. It allows the body to perform exercises with a full range of motion, which is key for fully engaging the muscle fibers, breaking them down, and ultimately building a stronger back. Furthermore, having flexible muscles can help prevent injuries that are common during strength training.
When your muscles, tendons, and ligaments are flexible, they can handle the strain of weight-bearing exercises more efficiently. For instance, when you perform deadlifts for your lower back, good flexibility can enhance your performance and reduce the risk of straining your muscles.
Stretching Exercises for Back
Various stretching exercises can enhance your flexibility, thus contributing to a stronger back. Here are some exercises you may consider:
- Child’s Pose: This yoga pose stretches the muscles of the lower back. Start by sitting on your knees, then stretch your hands forward along the floor as you lower your body. Hold the position for at least 30 seconds.
- Cat-Cow Stretch: This exercise targets the entire back. Get on your hands and knees and alternate between arching your back upward, like a cat, and sinking it downwards, like a cow.
- Trunk Rotation: Lie on your back with knees bent. Keep your feet flat on the floor, then slowly drop your knees to one side, keeping your shoulders on the floor. Repeat on the other side.
Ensure that all stretching exercises are performed slowly and through the whole range of motion. Do not rush or force any movement to avoid injury.
The Role of Resting in Muscle Growth
Rest is as crucial as exercise when it comes to building back muscle. When you exercise, particularly when resistance training, you create tiny tears in the muscle fibers. These tears are then repaired by your body while you rest, making your muscles stronger and bigger over time.
It’s during this rest period that your back muscles have the opportunity to recover and grow. That’s why it is essential to take rest days in between intense workout sessions. Adequate rest not only facilitates muscle recovery and growth but also helps prevent overtraining, injuries, and burnout.
The amount of rest needed varies between individuals. However, a general rule of thumb is to ensure you get at least 24 to 48 hours of rest before working the same muscle group again. Also, getting a quality night’s sleep aids in optimal muscle recovery.
In conclusion, achieving a strong back requires more than just performing strength-training exercises. It involves improving your flexibility through stretching and allowing your muscles sufficient time to rest and recover. By incorporating these elements into your workout regimen, you will be on your way to building a stronger and healthier back.

Nutrition for Muscle Growth
Nutrition and Muscle Growth: Protein Consumption
The building blocks for muscle are proteins, which are large molecules made up of amino acids. Consuming enough protein is vital for muscle growth and repair. The average adult needs at least 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. For those engaging in strength training exercises, this amount should be increased to 1.2-2.0 grams per kilogram. Ideal protein sources are lean meats like chicken, turkey, fish, and lean cuts of beef. Plant-based proteins, such as lentils, chickpeas, and tofu, are also an excellent choice.
The Role of Carbohydrates in Muscle Development
Contrary to popular belief, a diet aiming for muscle growth isn’t all about protein. Carbohydrates are equally important, as they provide the energy required for intense workouts. They also aid in the recovery process post-workout by replenishing muscle glycogen stores. Around 3-5 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight is recommended for those undertaking regular training. Healthy sources of carbohydrates include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
Healthy Fats: Unsung Hero of Muscle Growth
Healthy fats form an important part of muscle growth. They aid in the production of hormones, such as testosterone which is key for muscle growth. They also provide dense calories which can help in gaining muscle mass for those who struggle to get enough calories from protein and carbohydrates. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids) are healthy choices. These can be found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Hydration: The Crucial Factor
A large portion of the human body is made up of water, making hydration a critical aspect of any diet, not just for muscle growth but for overall health. Proper hydration helps in maintaining blood volume and providing the necessary environment for muscle cells to function at their peak during workouts. It also aids in the transport of nutrients to muscles. An average adult male needs about 3.7 liters of total water intake a day. This includes all beverages and food.
Tailored Diet Plan for Muscle Growth
While these guidelines give a general idea of the nutrients necessary for muscle growth, individual needs may vary based on age, gender, weight, metabolism, and workout intensity. Therefore, consider seeking advice from a dietitian or a fitness professional to create a tailored diet plan. Such a plan takes into account calorie needs, meal timing, and specific food choices, all optimized to accompany your workout regime and to maximize muscle strength and growth.

To undertake a journey towards a stronger back is no small feat, and putting in the physical work is only a part of the equation. Gaining an in-depth understanding of our back muscles, performing strength training exercises with correct form, incorporating cardio effectively, appreciating the importance of proper stretching and recovery days, and following a balanced diet play equal parts in molding a strong, resilient back. Equipped with this plethora of information, the next step forward is devising a balanced and well-rounded regime tailored to your unique needs. By doing this, not only will you be able to enhance your back strength, but you’ll also significantly improve your overall fitness, health and well-being.