In a society where digestive health is often overlooked, understanding the signs of an impacted bowel can be crucial for maintaining optimal health. A condition known as bowel obstruction, an impacted bowel happens when a blockage forms in the digestive tract, disrupting the body’s natural processes and potentially posing serious health risks. This comprehensive guide aims to enhance awareness about this condition, offering insights into its symptoms, common causes, ways of diagnosis, and available treatments.
Understanding What an Impacted Bowel Is
Understanding What an Impacted Bowel Is
An impacted bowel, medically known as a bowel obstruction, is a blockage that prevents matter from passing through the intestines as it normally would. The human digestive system is designed to process food, extracting nutrients and eliminating waste. After eating, the food travels from the stomach to the small intestine, where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients occur. The undigested residue, largely water, electrolytes and fiber, then moves to the large intestine or colon, where water is absorbed and feces are formed.
In the case of an impacted bowel, the passage of this waste material is blocked. This could happen in either the small intestine (small bowel obstruction) or the large intestine (large bowel obstruction). Impactions could be due to various reasons such as twists in the bowel (volvulus), adhesions (bands of scar tissue), hernias, tumors, swallowed objects, or diseases like Crohn’s and diverticular diseases.
Impacted bowel is a serious condition often requiring immediate medical attention. If left untreated, complications can arise such as tissue death, infection, or even a tear in the intestinal wall.
Signs of an Impacted Bowel
Early detection of an impacted bowel can expedite treatment and potentially reduce complications. People experiencing symptoms tied to a potential bowel obstruction should promptly contact their healthcare provider. The signs and symptoms of an impacted bowel will depend on the site and extent of the obstruction. They may be mild or severe, intermittent or constant.
Some common signs of an impacted bowel can include consistent abdominal pain or cramping, that may be severe. This pain is often due to the body’s attempts to overcome the blockage. Infrequent bowel movements or an inability to pass gas could also be telling signs of an obstruction.
Other symptoms may include a distended or swollen abdomen, nausea or vomiting, especially vomiting fecal matter in severe obstructions. Loss of appetite, constipation or diarrhea (in partial obstructions), and unexplained weight loss may also indicate bowel obstruction. In some cases, symptoms of dehydration like dry mouth, excessive thirst, or reduced urine output can be observed due to loss of fluid during vomiting or failure to absorb water in the colon.
Overall, any abnormal digestive symptoms enduring for several days should be a prompt for medical consultation. These signs are the body’s way of signaling that something is wrong, and in the case of an impacted bowel, prompt medical intervention can prevent serious complications.
Understanding the Severity of Bowel Impaction
Bowel impaction is a severe medical situation that can cause life-threatening consequences if not managed promptly. This condition happens when a physical blockade interrupts blood flow in a section of the intestine, leading to its death, medically known as ischemia. If left untreated, this can progress to a condition known as perforation, where a hole is formed in the intestinal wall, resulting in contamination and infection inside the abdominal cavity – a state known as peritonitis.
Bowel impaction can also progress to sepsis without proper treatment. This is a systemic inflammatory response to an infection which results in widespread clotting and problems with organ functioning.
Given the severity, it’s crucial to pay attention to the symptoms of bowel impaction and seek immediate medical help if they develop. Available treatments usually require hospitalization and may include non-surgical measures such as intravenous fluids, medication, and nasogastric tubes. Surgical interventions may be warranted depending on the severity and underlying cause of the impaction.
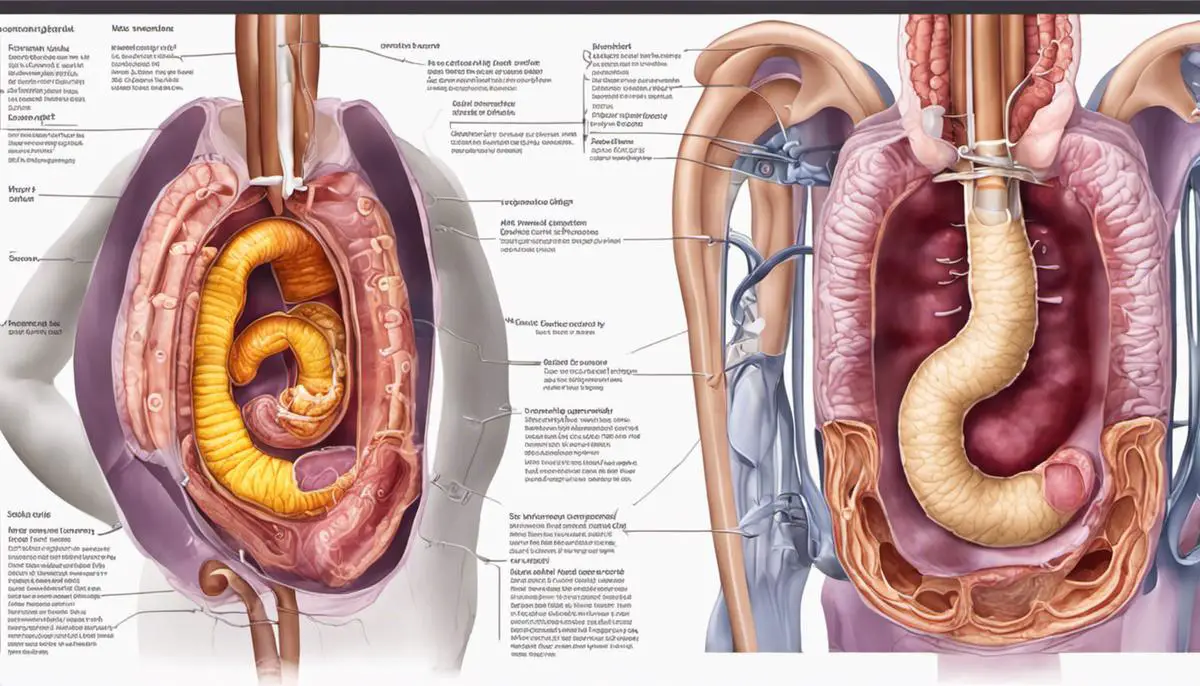
Symptoms of Impacted Bowel
Defining An Impacted Bowel
An impacted bowel or fecal impaction is a condition where hardened stool becomes immovable and gets stuck in the rectum. Often, it’s seen as a severe presentation of chronic constipation. However, it can also occur if there’s a problem with the muscles responsible for waste elimination. If these defecating muscles are weak or not functioning as they should, they can contribute to fecal impaction.
Common Symptoms of an Impacted Bowel
One of the most frequent indicators of an impacted bowel is chronic constipation. If you experience less than three bowel movements per week and have difficulty or discomfort passing stools, you might be suffering from constipation.
Abdominal pain is another common symptom. The location of the pain can vary but is most often felt in the lower left area of the abdomen. The pain usually worsens over time and may become severe.
Bloating and discomfort are also regularly associated with bowel impaction. An impacted bowel often instigates feelings of fullness and pressure in the abdomen, which can result in bloating or distension.
Vomiting can occur as a more severe symptom if the bowel impaction has disrupted the digestive system’s regular functioning.
Uncommon Symptoms of an Impacted Bowel
While the above-mentioned symptoms are more predictable, an impacted bowel may also cause less common signs such as unexplained weight loss, bladder issues, or even changes in behavior and memory in severe cases, particularly among older adults.
For instance, in some cases, fecal impaction may put pressure on the bladder, causing frequent urination, urinary incontinence, or even urinary retention in extreme cases.
Unexplained weight loss might occur because the affected individual is not absorbing enough nutrients due to the impaction or because they are eating less due to feelings of fullness or discomfort.
Recognizing the Signs of an Impacted Bowel
Being informed about the signs of an impacted bowel can prompt early medical attention, which is integral to preventing severe complications. You should consider consulting a doctor if you persistently suffer from constipation or if basic home remedies, such as increasing water and dietary fiber intake or using over-the-counter laxatives, aren’t effective. Severe abdominal pain, vomiting, unanticipated weight loss, and extreme constipation are all red flags that warrant immediate medical assistance.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to complex conditions like fecal impaction, which could escalate into serious complications like bowel obstruction, perforation, or fecal incontinence. Timely diagnosis and treatment can manage these symptoms efficaciously and prevent complications from occurring.
Since everyone’s digestive system varies, it’s crucial to be aware that what’s ‘normal’ is varied. So, when seemingly minor changes in bowel movements persist for weeks, or are paired with weight loss or bleeding, don’t hesitate to get professional medical advice.

Common Causes of an Impacted Bowel
Understanding the Causes of an Impacted Bowel
An impacted bowel, also referred to as bowel obstruction, may be attributed to numerous factors. These factors often disrupt the standard function of the digestive tract, leading to hard stool build-up that is challenging to expel. Recognizing these causes can help individuals identify potential risk factors linked to bowel impaction. These potential triggers might include lifestyle choices, genetic conditions, certain diseases, structural abnormalities, and other pertinent disorders.
Lifestyle choices can significantly affect bowel health. Insufficient physical activity, inadequate hydration, and a diet lacking fiber are habits that can lead to chronic constipation, a leading cause of bowel impaction. Inadequate exercise can slow down digestion, while insufficient water intake can harden the stool. Simultaneously, a diet low in fiber can cause small, hard stools that are difficult to pass.
Genetic predisposition can also play a role in bowel impaction. For example, individuals with cystic fibrosis are more prone to constipation and bowel blockage.
Specific diseases, such as conditions affecting the nervous system like Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke can disrupt the digestive tract’s normal functioning and lead to bowel impaction. Bowel cancer can also cause obstruction if a tumor grows large enough to block the passage.
Structural abnormalities, both congenital and acquired, can contribute to bowel impaction. This includes conditions like rectocele and intestinal malrotation.
Lastly, certain conditions, such as hypothyroidism and diabetes, which can respectively slow metabolism and damage the nerves controlling the digestive system, can also contribute to bowel impaction.
Identifying the Indicators of an Impacted Bowel
An impacted bowel is an urgent medical condition that should be addressed promptly to prevent complications. Common indicators of this condition cover a broad spectrum, including abdominal discomfort and bloating, a sensation of rectal fullness, trouble passing stools, lower back pain, sudden weight loss, weakness, vomiting, and alterations in bowel patterns—specifically, a strain during bowel movements. In some situations, extreme constipation or diarrhea could also signal a bowel obstruction.
Neglecting to treat an impacted bowel can lead to more severe symptoms like an accelerated heart rate, breathlessness, a high temperature, and even rectal bleeding. These are warning signs of potentially grave conditions such as bowel perforation or ischemia, a decrease in blood supply, both of which necessitate immediate medical intervention.

Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Detecting an Impacted Bowel: Diagnosis & Tests
If a patient presents with signs suggestive of an impacted bowel, the first step often involves a physical examination at the hands of a health professional. During this evaluation, the doctor may inspect your abdomen for any swelling or tenderness and listen to your digestive noises using a stethoscope to identify any unusual noises that could indicate a blockage.
A range of diagnostic tests might be performed to verify the presence of an impacted bowel. These could involve blood tests aiming to highlight inflammation markers, infection signals, or organ functioning indicators. A digital rectal examination might also be conducted where the healthcare provider checks for obstructive fecal matter using a gloved finger.
Advanced imaging tests like X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans or abdominal ultrasounds can be employed to gain a clear visualization of the colon and detect an impacted stool, physical anomalies or obstructions. In complex cases, a colonoscopy may be suggested—this procedure uses a flexible tube equipped with a light and camera, inserted into the rectum to thoroughly examine the inside of the colon.
Treatment Options: Gradual Steps toward Resolution
Treating an impacted bowel often starts with conservative, at-home remedies. This includes dietary changes such as increasing intake of fiber-rich foods and fluids to help soften stool and promote regular bowel movements. Regular physical activity can also stimulate intestinal contractions and support digestion.
If these steps are not sufficient, over-the-counter remedies may be suggested. Stool softeners, laxatives, and enemas can facilitate the passage of stool. However, these should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider to avoid potential complications.
For severe impaction, especially those with complications, a healthcare provider may conduct a manual disimpaction. This procedure involves the physical breaking up and removal of stool from the rectum and is typically done under anesthesia.
In urgent cases where conservative measures are unsuccessful, surgical intervention may be necessary. This can involve the removal of the impacted stool or in extreme cases, removal of affected portions of the colon.
It’s worth noting that an impacted bowel is often a sign of chronic constipation. Therefore, a comprehensive treatment plan often includes measures to prevent further impaction. This may involve long-term dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, or in some cases, prescription medications that promote regular bowel movements.
Throughout the whole process, it’s essential for patients to remain closely in touch with their healthcare provider, who can help them navigate treatment and potentially prevent serious complications, such as infection or tears in the intestinal wall.
Being informed and mindful of the health of our digestive system, specifically recognizing the signs of an impacted bowel, can equip us with the knowledge to seek timely medical assistance. Moreover, identifying the common causes of this condition and understanding its treatment options can be the first step towards maintaining our overall well-being. Armed with this knowledge, every person can make informed decisions about their health and take appropriate steps to ensure a healthy and functioning digestive system. As we become more proactive about our health, we not only contribute to our individual well-being but to a healthier society as well.
