Understanding the workings of the body, specifically the digestive system, is crucial to maintaining overall health and wellbeing. We often take our body’s complex mechanisms for granted until things go awry. One such concern that many people experience, yet rarely discuss, is the issue of ‘stuck poop’, or in formal terms, constipation. This condition can not only be discomforting but can also indicate deep-seated health issues. This article will delve into intricacies of the digestive system, specifically focusing on the large intestine, to understand the normal process and timing of digestion, and why issues with stool release might occur.
Understanding the Digestive System
Understanding the Digestive System and Stool Production
The digestive system is a complex, multi-part mechanism that breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and disposes of waste. It starts from the mouth, proceeds to the esophagus, then to the stomach, small intestine, and finally to the large intestine or colon.
Food is broken down in the stomach and the nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine. The leftover waste, which includes undigested parts of the food, fiber, and cells shed from the lining of your guts, gets passed into your large intestine. Here, an average of 36 hours is spent during which water and electrolytes are absorbed back into the body and the semi-liquid waste material is solidified to form feces or poop.
Stool Transit and Release
A special type of movement called peristalsis pushes the feces through the large intestine, towards the rectum, and out through the anus during a bowel movement. The timing of these bowel movements can vary greatly between individuals – some people may have more than one motion a day, while others may have them every other day or so. The consistency of the stool can also be influenced by diet, hydration, stress, certain medications, and physical activity.
Dealing with Constipation
When poop gets stuck, it means that the stool is not being effectively pushed out of the body. This is often due to constipation, a condition characterized by infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stool, and often, discomfort and bloating.
There are several reasons why constipation can occur. Some of the most common include a diet low in fiber, inadequate fluid intake, lack of physical exercise, and ignoring the urge to pass stool. Some medications and health conditions can also contribute to constipation.
Persisting Poop Problems
In some cases, the stool may become too hard or too large to pass out of the body comfortably — a condition often referred to as fecal impaction. This is a severe form of constipation that may require medical intervention.
In more serious cases, a blocked stool might also indicate an underlying health concern such as colorectal cancer or a bowel obstruction, both of which can cause severe complications if left untreated. Therefore, if constipation or difficulties passing stool persist for more than a few days, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
Tackling the mystery of why our poop can sometimes get lodged is prominently reliant on a comprehensive understanding of our digestive system and its intricate processes. Recognizing potential impediments in our digestive cycle betimes and promptly seeking appropriate treatment are paramount to maintaining our overall health. An amalgamation of factors, including diet, hydration, lifestyle habits, and prevailing health conditions significantly influence the constitution and release of our poop.
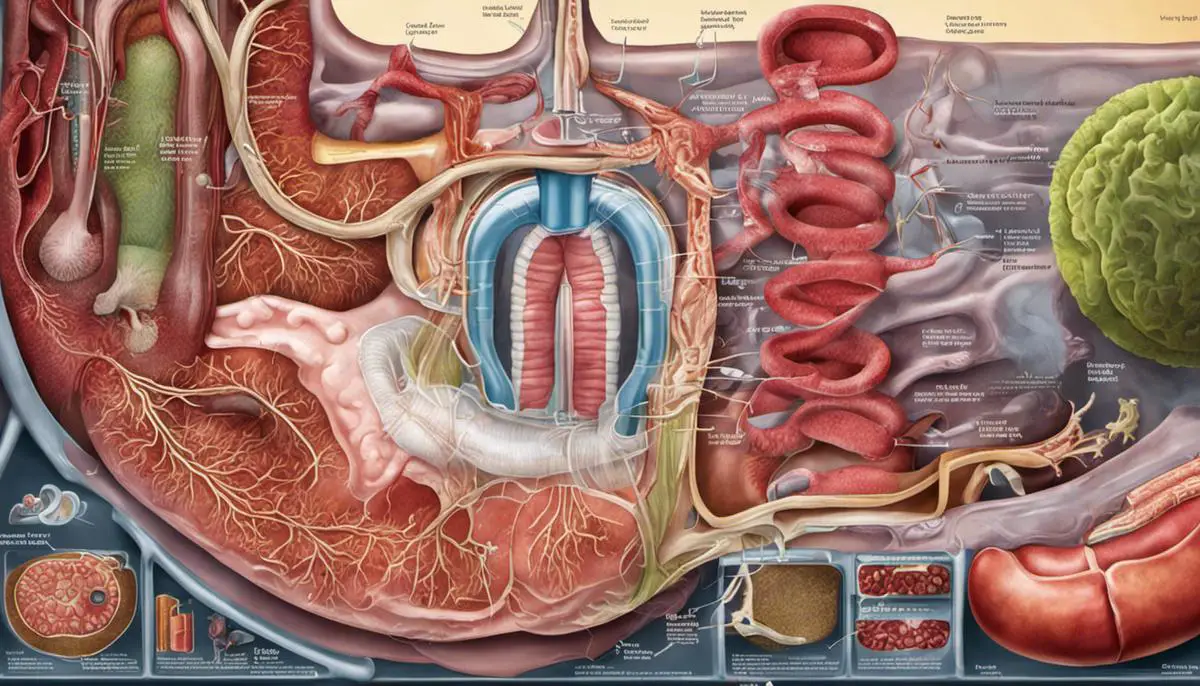
What is Constipation?
Highlighting Constipation
A common culprit responsible for the phenomenon of ‘stuck’ poop is constipation, an ailment that creates hitches in your digestive mechanism, bringing about difficulties in discharging your bowels—generally characterized by hardened stool. This leads to uncomfortable fullness or bloating, fostering the sensation of unfinished bowel movements or ‘stuck’ poop.
Constipation’s manifestation varies amongst individuals. Some are plagued by its presence occasionally, while chronically for others, causing substantial pain, discomfort and impacting life quality. It’s crucial to note that the frequency of normal bowel movements fluctuates significantly—from those who experience up to three per day to others who only endure one or two per week.
Various Types of Constipation
There are different types of constipation – chronic constipation, occasional constipation, and chronic idiopathic constipation.
Chronic constipation is diagnosed when an individual experiences constipation-related symptoms, like less than three bowel movements a week, straining during bowel movements, or a sense of incomplete evacuation, for several weeks.
Occasional constipation, on the other hand, is characterized by infrequent bowel movements or difficulty passing stools that lasts for a few days.
Chronic idiopathic constipation is a diagnosis reserved for severe constipation symptoms that have no identifiable root cause and lasts for several months.
Common Causes of Constipation
Understanding the causes of constipation can help a person to manage or even prevent this uncomfortable condition. Causes can range from lifestyle factors, dietary choices, and even certain medications.
One of the most common causes of constipation is lack of fiber in the diet. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass. When a diet is low in this key nutrient, stool can become hard, dry, and difficult to pass, causing constipation.
Dehydration is another common potential cause. Without adequate fluid intake, the colon absorbs water from the stool, making it hard and dry, which can result in constipation.
Lack of physical activity or sedentary lifestyle is also associated with an increased risk of constipation. Exercise helps increase the action of the muscles in your intestines, promoting bowel movements.
Certain medications can also result in constipation. These include certain pain medications like opioids, antacids, anti-depressants, and specific blood pressure medications, among others.
In some instances, constipation may be caused by medical conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diabetes, thyroid disorders, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurological conditions.
Understanding the Phenomenon of ‘Stuck’ Poop
Imagine this: you’re frequently confronted with hard, dry stools that seem to get ‘stuck’ in your system, leaving you feeling bloated and uncomfortable. This is called constipation, a common issue characterized by sparse, challenging bowel movements. It signifies that your body isn’t correctly processing the food and liquids you consume. When your stool loses its normal, soft consistency and becomes compacted, it’s more difficult for your body’s muscles to push it through your intestines and eventually out through the rectum. While occasional constipation can be a regular part of life, chronic constipation is a sign that something is not right with your digestive health. If you notice severe symptoms such as bloody stools or unexpected weight loss accompanying your constipation, it’s crucial to consult with a medical professional.

Photo by chrisjoelcampbell on Unsplash
Signs and Symptoms of Constipation
Recognizing the Symptoms of Constipation
It’s essential to know the signs of constipation to catch it early and take appropriate action. Typical symptoms include hard, dry and lumpy stools that are challenging to pass as well as a feeling of not emptying the bowel completely even after passing stool. Some people may also feel a blockage in the rectum or experience difficulty and strain during bowel movements. These are the reasons why it feels like your poop is ‘stuck.’
Remember, everyone’s body is different – while some might have a bowel movement every day, for others, every two or three days is normal. However, going more than three days without a bowel movement is usually a sign of constipation. After this time, the stool hardens and becomes even more challenging to pass.
Possible Causes of Constipation
While there are numerous potential causes of constipation, some of the most common include not eating enough fiber, not drinking enough fluids, lack of exercise, changes in lifestyle or routine, including eating habits, and ignoring the urge to poop. These can lead to reduced bowel activity, causing the stool to move slowly and dry out, leading to constipation and the sensation of ‘stuck’ poop.
Certain medical conditions can also predispose an individual to constipation. For instance, neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease, metabolic and endocrine disorders such as diabetes or hypothyroidism, and systemic conditions like lupus can all lead to constipation.
Furthermore, specific medications like antacids, antispasmodics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and certain pain medications can impact bowel motility, leading to constipation.
Understanding Chronic Constipation
Chronic constipation is a more persistent form of constipation that can significantly hinder a person’s quality of life. In some cases, it may not respond to standard treatments. Chronic constipation could be due to an underlying medical condition, such as a hormonal imbalance, or a bowel function disorder.
If you regularly experience symptoms of constipation and find difficulty passing stool over extended periods, it’s essential to see a healthcare provider. Persistent constipation may indicate a more severe problem, such as colorectal cancer, anal fissures, hemorrhoids, or bowel obstruction.
Treatment and Prevention of Constipation
The treatment and prevention measures for constipation usually focus on lifestyle adjustments. This could include dietary changes, such as increasing the intake of fiber-rich foods, drinking plenty of fluids, and engaging in regular physical activity.
Over-the-counter remedies like fiber supplements or stool softeners could also be beneficial. In more severe instances or for individuals with chronic constipation, prescription medications or surgical procedures may be necessary.
In Summary
Experiencing a sensation of ‘stuck’ feces could be an indication that you are suffering from constipation. Increasing your awareness of this condition’s signs, symptoms, and potential causes, may prompt you to make necessary lifestyle modifications or consult with a medical professional if required.

Potential Serious Causes for Stuck Poop
Potential Serious Causes for Stuck Poop
While having an occasional issue with ‘stuck poop’ is a phenomenon that many individuals often encounter, predominantly due to dietary choices or irregular daily routines. In some occurrences, it could be a symptom of a more serious underlying health problems like colon cancer or bowel obstruction.
Generally, constipation is identified by having less than three bowel movements a week, experiencing difficulty during evacuation, or feeling like you couldn’t empty your bowels completely. Although constipation can be both an inconvenience and discomfort, it’s usually not deemed dangerous. However, if constipation extends for several weeks, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider because it may be indicative of a more grave health concern.
Colon Cancer
One of the potential serious causes of constipation might be colon cancer. Colon cancer affects the large intestine and usually begins as small, benign clumps of cells called polyps. Over time, some of these polyps can develop into colon cancers.
Long-term constipation may be a symptom of colon cancer. Other symptoms can also include rectal bleeding or blood in the stool, persistent abdominal discomfort, weakness or fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. If colon cancer is suspected, clinicians can conduct a series of tests including blood tests and colonoscopies to confirm the diagnosis. Early detection is crucial in the treatment of colon cancer.
Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstruction, another potential cause of ‘stuck poop’, is a blockage that prevents the contents of the intestines from passing normally through the digestive tract. The two types of obstruction are mechanical and functional. A mechanical obstruction occurs when the bowel is physically blocked, often by a tumor, scar tissue or a twisting of the intestine. Functional obstruction, or paralytic ileus, happens when the muscles that push the contents through the bowel stop working.
Symptoms of a bowel obstruction can include periodic episodes of severe abdominal cramps, frequent bouts of constipation, decreased appetite, and swollen abdomen. If a bowel obstruction is suspected, a medical professional will typically perform a physical exam, imaging tests, and possibly surgery to diagnose and treat the problem.
If you are faced with the issue of ‘stuck poop’ or occasional constipation, it’s good to know that this predicament can often be solved with lifestyle modifications or over-the-counter aids. However, if these symptoms persist or are accompanied by other worrying signs, it’s vital to reach out to a healthcare professional for an appropriate diagnosis and to treat potential serious underlying health concerns timely.
Photo by jessedo81 on Unsplash
Methods to Alleviate Constipation
Shedding Light on Constipation
When you ask, “Why is my poop stuck?”, the medical community may describe this as constipation. This prevalent digestive disorder is defined by infrequent evacuations, hardened or dry stools, and difficulty or straining during defecation. Constipation can be triggered by various factors including poor dietary habits, side effects of medicines, sedentary lifestyle, or pre-existing health conditions.
Home Remedies for Constipation Relief
One of the simplest ways to alleviate constipation is through home remedies. Simply increasing your daily water intake can make a big difference since dehydration often leads to constipation. Another remedy involves drinking warm liquids, like tea or warm water with lemon, especially in the morning. This can help stimulate your digestive system. Foods that are high in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are also beneficial in alleviating constipation.
Importance of Exercise
Regular physical activity has been linked to significant improvements in digestive function, including alleviating constipation. When the body is actively moving, it encourages the intestines to move and expel waste more efficiently. Regular exercises like walking, jogging, swimming, or yoga can stimulate the muscles in the bowels, leading to regular, softer, and easier-to-pass stools.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
There are also over-the-counter remedies that can assist with easing constipation. Oral fiber supplements like psyllium husk or methylcellulose can be consumed daily to add to dietary fiber intake. Stool softeners work by increasing the water content in the stool making it softer and easier to pass. Laxatives help stimulate the intestines to move to pass stools. Always remember to use these products as directed by the manufacturer or your healthcare provider.
When to See a Doctor
While occasional constipation is common, persistent symptoms may signal an underlying medical condition. Visit a healthcare professional if you experience sudden changes in bowel habits, severe abdominal pain, blood in the stool, or if constipation persists despite lifestyle changes and over-the-counter remedies. The physician may prescribe additional treatments or conduct tests to determine a suitable treatment approach. Medical treatments can include prescription drugs, biofeedback therapy, or, in severe cases, surgical interventions.

Whether it’s a fleeting issue or a lasting dilemma, understanding what’s going on inside your body is the first step towards leading a healthier life. Digestive disorders like constipation aren’t a rare occurrence, but continuous inaction and negligence of your body’s warning signs could potentially give rise to more serious health threats. Amidst understanding the causes and symptoms, remember that preventative measures and treatments are just as crucial. From home remedies to dietary changes, to the use of prescribed treatments, there are several routes available to help treat constipation. A step in any of these directions could bring the much-needed relief and lead to better bowel health in the long run.
