Fostering a strong and stable lower back is an integral component of holistic health and wellness. Many individuals grapple with lower back discomfort and its incapacitating repercussions. With an enhanced understanding of the lower back anatomy, it’s possible to tackle this issue through Aerobics – a robust and practical approach. This science-based strategy focuses on learning about muscles and spine structure, safety guidelines to prevent injuries while performing aerobics, and identifying ideal workouts for lower back strength and flexibility. In addition, it offers insights into designing an effective aerobic routine, integrating factors of duration, intensity, and frequency, thereby adding an engaging variety to your workouts.
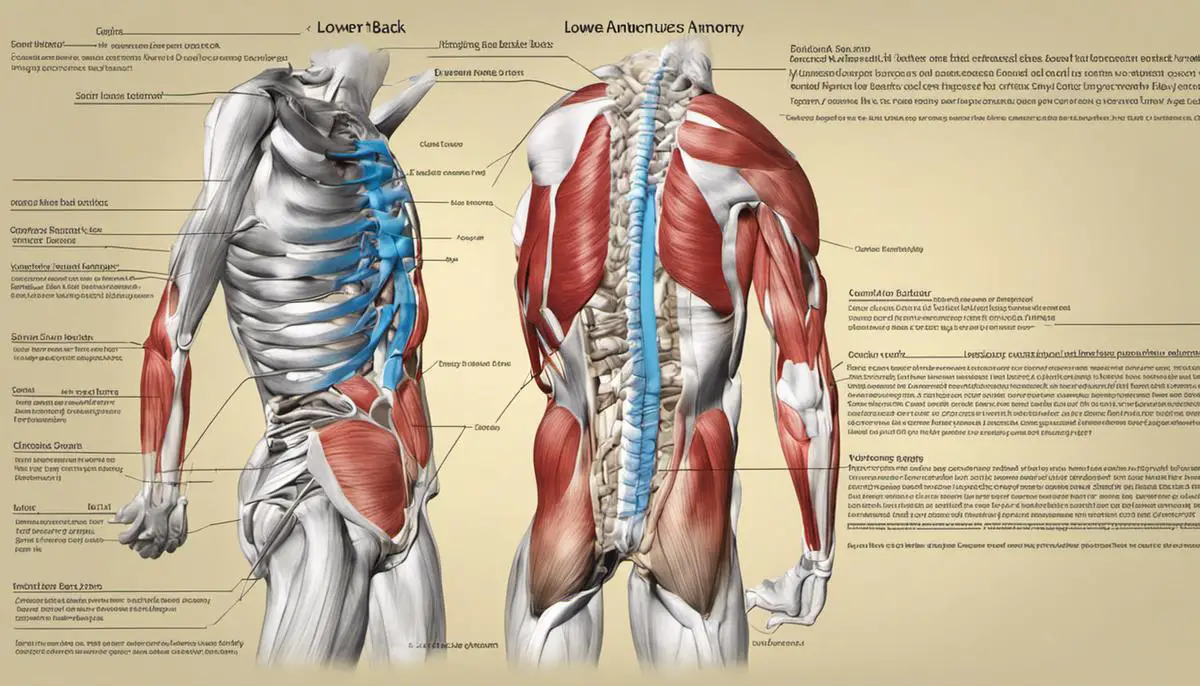
Understanding Lower Back Anatomy
Understanding Lower Back Anatomy: Spinal Structure
The lower back, or lumbar region, is made up of five vertebrae, labeled L1-L5. These are the largest and strongest vertebrae in the spine, capable of carrying most of the body’s weight. They are stacked on top of each other separated by intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers. These vertebrae are unique in their design, as they combine strength and flexibility, allowing for a great range of motion, while also acting as a protective structure for the spinal cord.
The Role of Muscles in Lower Back
The multitude of muscles around the lower back provides support, strength, and flexibility to the spine. Some of the main muscles in this region include the Latissimus Dorsi (often referred to as the ‘lats’), which are large muscles in the lower back, and the Erector Spinae, which run vertically along the back of the spine. These muscles, along with the Quadratus Lumborum and various smaller muscles, help stabilize the spine, assist with rotation and lateral movement, and support the body in maintaining an upright posture.
Understanding the Role of Ligaments and Tendons
Ligaments and tendons also play a critical role in lower back structure and function. Ligaments are tough, fibrous tissues that connect bones to other bones, providing stability to the joints. In the lower back, the Anterior and Posterior Longitudinal Ligaments run vertically along the front and back of the vertebral bodies, providing substantial support and stabilization for the lumbar spine.
Tendons, on the other hand, connect muscles to bones. In the lower back, the tendons of numerous muscles attach at various points on the lumbar vertebrae, maintaining the alignment of the spine and assisting in a variety of movements, such as bending and twisting.
Knowing your lower back: The role of nerves
The lumbar spine also includes a complicated network of nerves. These nerves exit the spine from small openings called foramen and transmit messages between the brain and the lower half of the body. Any kind of pressure or pinch on these nerves may lead to lower back pain or conditions like sciatica.
In strengthening the lower back through aerobic exercises, it is essential to understand the function of these anatomical structures. This understanding will aid in creating a balanced regimen that properly targets these areas without causing injury. Exercises focusing on the lumbar region will engage and strengthen these muscles, enhance the stability provided by the ligaments and tendons, and contribute to your overall lower back health.
Safety Guidelines & Injury Prevention
Safety Guidelines for Lower Back Strength Aerobics
To practice aerobics for strengthening your lower back safely, firstly, always remember the importance of maintaining correct form. Maintaining proper posture during each of the various aerobic exercises is absolutely vital in preventing injuries. This involves keeping your spine aligned, core engaged, shoulders back, and chest lifted.
When the form is off, or incorrect, it places unnecessary strain on your muscles, increasing the risk of tears, strains and, in worse cases, serious injuries. Ensure that your movements are smooth and controlled; jerking or rushing through movements can cause undue stress on the lower back.
Warm-Up Drills
Before starting with aerobics, it is crucial to have a proper warm-up session. This helps to gradually increase your heart rate and circulation, making the muscles ready for the rigors of your work out, thereby minimizing the risks of injury.
You can start with a light cardio routine such as walking or jogging in place for about 5-10 minutes until your body feels warm. Follow this up with dynamic exercises that mimic your routine like deep lunges, knee high runs, or leg swings.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching as a pre-aerobic activity prepares your muscles for the workout session while post-aerobic stretching helps to cool down your muscles. Stretching increases the flexibility of your body reducing your chance of an injury.
Regular lower back stretches you might want to consider include the seated lower back rotational stretch, the knee to chest stretch, and the draw-in manoeuvre. Always remember to hold your stretches for about 30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times for each stretch.
Cooling Down Exercises
Similar to warm-up drills, cooling down after your aerobic exercises is also essential in preventing injuries. It helps to gradually reduce your heart rate to its normal level and prevents the pooling of blood in your lower extremities which might lead to dizziness.
Simple cooling down exercises may be as simple as walking on the spot or a gentler version of your aerobic routine for 5-10 minutes, followed by stretches focusing on your lower back and the muscle groups you worked during your session.
Injury Prevention Techniques
Apart from maintaining correct form and warming up, other injury prevention techniques include listening to your body. Don’t push beyond your limits. If you feel pain or strain in your lower back during the exercise, stop and rest. Wear appropriate footwear to protect your feet and provide good support for your lower back. Always stay hydrated and stop the workout if you feel dizzy or severely out of breath.
Lastlly, regular strength training exercises can help to augment your lower back muscles and provide better support, thereby reducing the risk of back strain during aerobic exercises. Remember to always consult a fitness professional if you’re new to aerobic exercises, particularly if you’ve had previous lower back issues.
Aerobics Exercises for Lower Back
Understanding Lower Back Strength and Flexibility
Lower back strength is crucial for maintaining good posture, avoiding injuries, and performing daily activities. Aerobic exercises that target the lower back area helps in increasing flexibility, promoting correct alignment, reducing pain, and enhancing overall fitness levels.
Low-Impact Aerobic Exercises
Pelvic Tilt
Pelvic tilt exercises can improve flexibility and help maintain a neutral spine. To do this exercise, lay on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Tighten your abdominal muscles, flatten your back against the floor, and tilt your pelvis upwards. Hold for 10 seconds and repeat 10 to 15 times.
Bird-Dog Exercise
Begin on your hands and knees with your hands directly below your shoulders and your knees directly below your hips. Extend one leg and the opposite arm, keeping your pelvis stable. Maintain this position for a few seconds, then return to your initial position. Do the same with the other arm and leg. Repeat the steps for 10 to 15 times per side.
High-Impact Aerobic Exercises
Jumping Jacks
Stand with your feet together and arms at your sides. Jump while spreading your legs and lifting your arms above your head. Land softly on your feet and immediately jump again. This exercise not only raises your heart rate but also strengthens multiple muscle groups, including the lower back.
Burpees
Start in a standing position, drop into a squat, place your hands on the ground, and jump your feet back into a plank position. Jump your feet back underneath you, return to a squat, and then jump into the air with your hands reaching towards the sky. Burpees are vigorous but work several muscle groups at once, including your lower back muscles.
Integrating Aerobic Exercise into Your Routine
Incorporate these exercises into your workout routine for comprehensive lower back support. Start with low-impact exercises and gradually add high-impact options as your lower back strength and flexibility improve. Ideally, aim for at least 30 minutes of aerobic exercise on most days of the week. Always consult a fitness professional or physical therapist before starting any new exercise regimen, particularly if you have a history of back pain or other injuries.

Aerobic Routine Design
Understanding the Basics of Aerobic Routine Design
When crafting an aerobic routine for lower back strength, it’s essential to combine different exercises into a holistic workout that targets the muscles effectively. The three crucial components to consider in your routine are duration, intensity, and frequency.
The Duration of Your Aerobic Exercises
The length of your workout routine plays a significant role in achieving your fitness goals. A good starting point is to aim for a 20 to 30-minute session. As you build endurance, gradually increase the duration to avoid putting unnecessary strain on your back.
Understanding Workout Intensity
Intensity speaks to how hard you’ll be working during your aerobic workout. For lower back strength, you should aim for moderate intensity. The idea is to engage your muscles without straining them, always maintaining a balance.
Frequency Is Key in Your Aerobic Routine
Create a workout plan that allows you to do aerobic exercises about three to five times a week. Allow for rest days in between to give your muscles the necessary time to heal and strengthen.
Building Variety Into Your Aerobic Routine
To prevent a plateau in your progress and keep your workouts engaging, build variety into your routine. You can alternate between exercises like bridges, back extensions, pelvic tilts, and bird dogs to target different muscles in your lower back and core.
Sample Aerobic Routine for Lower Back Strength
Here’s a sample routine:
- Warm up with light cardio for five minutes.
- Do a set of 10 bridges, lying flat on your back with knees bent and lifting your hips.
- Follow up with 10 back extensions. Lie on your stomach and lift your chest off the floor.
- Try 10 pelvic tilts, lying on the floor with knees bent and tilting your hips towards your chest.
- Finish with a set of 10 bird dogs, starting on all fours and extending one arm and the opposite leg.
- Repeat the sequence for the desired number of sets.
- Cool down with five minutes of stretching exercises.
For each exercise, make sure you’re engaging your core muscles and always maintain proper form to reduce the risk of injury. Adjust the number of sets and repetitions according to your fitness level.
Designing Additional Aerobic Routines
To build additional aerobic routines, choose various exercises that target different muscle groups in the lower back and core. You may want to incorporate other forms of cardio, like walking or cycling, to improve overall endurance. Be sure to change your routines every couple of weeks to keep challenging your muscles. Always maintain a balance between duration, frequency, and intensity for the best results.

Photo by rimakruciene on Unsplash
Armed with an appreciable understanding of the lower back anatomy and safety guidelines, sophisticated lower back workouts and innovative aerobics routines, the journey towards enhanced lower back strength no longer seems daunting. Consistent and correctly-executed aerobic exercises will not only fundamentally strengthen the lower back but also augment the overall posture and flexibility. As individuals venture on this path of health and wellness, adopting these aerobic practices will be instrumental in achieving their lower back strength goals, profoundly improving their quality of life and well-being.