In daily life, we often ignore small changes in our body and fail to realize that they may be reflecting our overall health. Such is the case with hard stool, a common issue afflicting many people, which can occur due to various dietary, medicinal, and health-related reasons. This comprehensive guide aims to educate readers on the different factors that cause hard stool ranging from the food we consume to our lifestyle choices and even underlying health conditions. Whether it’s the effects of eating a low fiber diet or dehydration, how our stress and exercise levels can affect bowel regularity, the impacts of certain medications or medical issues, there is no stone left unturned in our bid to raise awareness about these seemingly minor, but critical health aspects.
Dietary Factors Affecting Stool Consistency
Dietary Factors Affecting Stool Consistency
People’s daily eating habits and the types of foods they consume can significantly impact their digestive system’s health and efficiency, including the consistency of their stool. One main dietary factor that can lead to hard stools is a low intake of dietary fiber. Fiber is a substance found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which the body’s enzymes cannot digest. Dietary fiber has a vital role in stool formation and passing. It helps to add bulk and softness to the stool, hence promoting regular bowel movements. When you do not consume enough fiber-rich foods, your stool may become hard, dry, and difficult to pass, leading to constipation. A few fiber-rich foods to include in your diet are fruits (such as pears, berries, and apples), vegetables (like carrots, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts), whole grains (such as brown rice, oatmeal, and whole-grain bread), and legumes (like beans, lentils, and chickpeas).Dehydration and Hard Stools
In addition to dietary fiber intake, adequate fluid consumption also plays a crucial role in stool consistency. When a person suffers from dehydration, their body tries to conserve water, causing the colon to absorb more water from the stool. As the stool loses water, it becomes harder and more challenging to pass. Therefore, drinking enough fluids – especially water – can help prevent dehydration and consequently hard stool. Alcohol and caffeinated beverages, in contrast, can lead to dehydration, disrupt regular bowel movements, and ultimately result in hard, dry stools.Lifestyle Habits and Hard Stools
Beyond dietary considerations, certain lifestyle habits can also contribute to hard stools. Lack of physical activity, for example, can slow down the digestive system, making it more difficult for the body to pass stool. Similarly, ignoring the natural urges to defecate can have the same effect by making the stool stay in the colon for a long time, causing it to dry and harden.People’s eating habits, daily routines, and health screenings play crucial roles in digestive health and stool consistency. Consuming a balanced diet with sufficient fiber, staying hydrated, and keeping physically active can significantly reduce the risk of having hard stools. Regular health check-ups also help in detecting any potential health issues that could ultimately result in hard, difficult-to-pass stools, a condition which can be both uncomfortable and painful.
Medication and Lifestyle Factors
The Impact of Medications on Stool Consistency
Certain medications can drastically affect stool consistency, and are known to result in hard stools. Antidepressants, for one, can slow down the digestion process by influencing the nerves and muscles in the large intestine. This slowdown allows more water to be reabsorbed back into the body, which leads to dry, hard stool.
Iron supplements, another common cause of hard stools, can cause constipation, especially when consumed in large quantities. These supplements interact with other elements in the digestive tract, forming a mass that can be difficult to pass. Despite its crucial role in blood health, it is recommended to discuss the appropriate iron dosage with a healthcare professional to avoid such side effects.
Even over-the-counter medications can lead to hard stools. Certain antacids containing calcium or aluminum can contribute to constipation, while allergy or cold medications that include antihistamines can slow intestinal movement, resulting in a harder stool. Similar effects can be caused by medications like anti-seizure drugs and pain relievers.
Factors Affecting Stool Hardness: Lifestyle and Habits
Various lifestyle factors have a direct impact on our stool consistency, one of them being physical activity. More sedentary lifestyles can lead to a sluggish digestive system and cause longer time for stool to stay in the large intestine. As a result,more water is reabsorbed back, making the stool hard and dry. On the other hand, regular physical activities can stimulate intestinal muscles and promote regular bowel movements, thus preventing hardness in stool.
Besides this, our mental health, especially stress levels, can also directly affect our digestive system. Chronic stress can cause changes in the functioning of our guts, either accelerating or slowing down the digestive process. Slower digestion allows more water to be reabsorbed from the stool making it drier and harder to pass.
Staying well-hydrated and following a wholesome diet, with an emphasis on high fiber content, are crucial to having regular and healthy bowel movements. Lack of adequate hydration can result in harder stools as the body struggles to maintain a sufficiently moist fecal matter. Similarly, lack of fiber in the diet makes the stool hard as this vital nutrient helps in water retention and adds bulk to the stool, avoiding constipation.
Moreover, habits such as smoking, consuming caffeinated beverages, or drinking alcohol may also lead to harder stools. These substances can cause body dehydration, disrupting the balance of fluids in the intestines and eventually hardening the stool.
This detailed examination of lifestyle factors and their effect on stool consistency shows us the multiple ways in which habits, behaviors, and choices can result in hard stools. It also highlights the importance of adopting a holistic approach for improving digestive health.

Photo by aweilguny on Unsplash
Underlying Medical Conditions
The Role of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) in Hard Stool Formation
Another factor that can contribute to the issue of hard stools is the presence of disorders like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). IBS is a common condition that affects the large intestine and comes with symptoms such as cramping, bloating, and abdominal discomfort, including changes in bowel movements like diarrhea and constipation. In people with IBS, changes in gut motility often result in hard stools. Triggers for IBS include certain foods, stress, hormonal fluctuations or other diseases.
Managing IBS requires a combination of lifestyle alterations, dietary modifications, and generally, medication. To make stools softer, increasing consumption of foods high in fiber is recommended. Engaging in regular physical activity can also spur contractions in the intestine and counter constipation. Medications may also be utilized to regulate bowel movements and to ease any painful symptoms.
Colon Cancer and Hard Stool
Colon cancer, which begins in the large intestine, at times manifests as a change in bowel habits, including the development of hard, narrow stools. This is due to a tumor narrowing the colon, which makes it harder for stool to pass through. Other symptoms include blood in the stool, persistent abdominal discomfort, and unexplained weight loss.
Reducing risk factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, and a diet low in fiber and high in fat can help prevent colon cancer. Regular screening tests for early detection of colon cancer—such as colonoscopies, virtual colonoscopies, and stool tests—are particularly important after the age of 50 or for those with a family history of the disease.
Hemorrhoids and Hard Stool
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus, often resulting from straining during bowel movements or pressure added to these veins during pregnancy. With increased straining, the passing of hard stool can exacerbate hemorrhoids, leading to pain, discomfort, or bleeding during defecation.
To prevent or treat hemorrhoids, individuals should aim to consume a high-fiber diet, stay hydrated, avoid straining during bowel movements, and not delay the urge to pass stool. Medications or surgical procedures might be necessary for severe hemorrhoids.
Hyperthyroidism and Hard Stool
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the thyroid gland produces an excess amount of thyroid hormones, speeding up the metabolism and causing symptoms like weight loss, rapid heart rate, and nervousness. While less common, hyperthyroidism can also lead to bowel-related symptoms, including diarrhea, frequent bowel movements, and possibly hard stool if dehydration occurs.
Treatments for hyperthyroidism may include thyroid hormone replacement, antithyroid medications, or radioactive iodine therapy, all aimed at restoring the normal function of the thyroid.
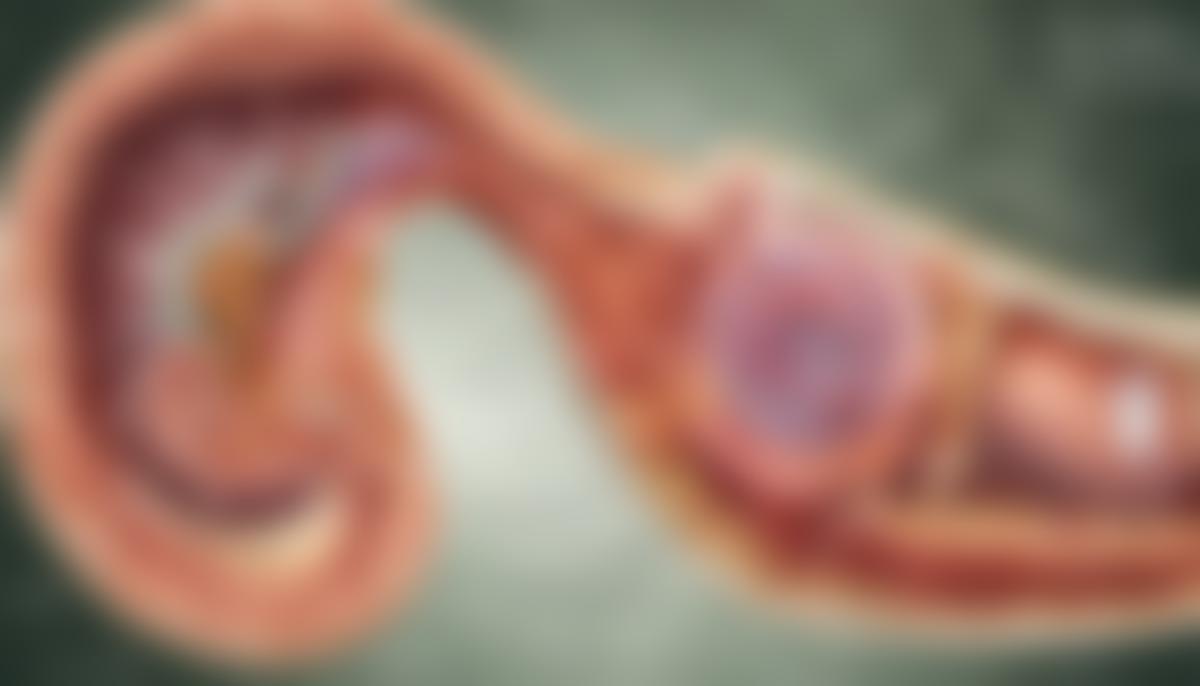
Hard stool can be a casual, occasional inconvenience or a symptom of more severe digestive concerns. The variety of factors contributing to this problem underscores the importance of paying attention to changes in our bodies, what we consume and how we live. A healthier lifestyle, appropriate medication control, and active identification and treatment of any underlying medical conditions can help in preventing or managing this issue. Hence, while addressing hard stool, one must consider all these facets to have the best chance of successful results. Through this guide, we hope we have empowered you with the insights needed to better manage this issue and, by extension, your overall wellbeing.
