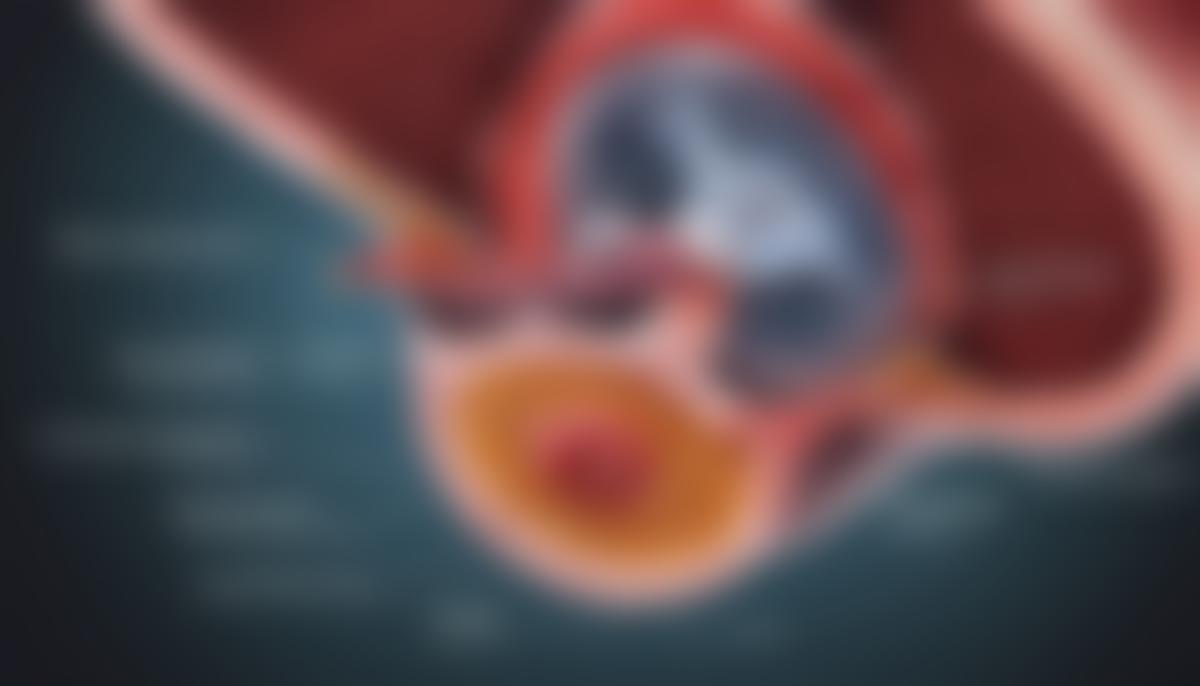
The prostate, a small gland found only in males, plays a critical role as part of the reproductive system. Acting as a key contributor to semen production, its health and functionality are of significant importance to a man’s overall well-being. Unfortunately, it is susceptible to a series of disorders, among which include prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and prostate cancer. Each of these poses unique challenges, symptoms, and potential risks if left unattended. Their diagnosis and treatment also require the utilization of specific medical tests and procedures. Equally essential is the understanding of preventive measures and strategies to aid in the maintenance of prostate health.
Understanding the Prostate and its Functions
Understanding the Prostate and its Functions
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland that forms part of the male reproductive system. It is located below the bladder, in front of the rectum, and surrounds the urethra — the tube carrying urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Primarily, the prostate produces a significant portion of the fluid that makes up semen — the milky substance containing sperm that is ejaculated from the penis during sexual climax. This fluid, rich in enzymes, proteins, and minerals, nourishes and protects sperm as it travels toward fertilization.
This gland is under the control of the male hormone testosterone, produced by the testicles. Testosterone influences the growth and function of the prostate, and alterations in its levels can impact the gland.
The prostate also has a strategic anatomical role in controlling urination. It includes muscular tissue that helps push semen through the penis during ejaculation. Additionally, the prostate and the surrounding tissues contract and press shut the opening between the bladder and urethra to prevent urine leakage during sexual stimulation.
Prostate Health and Disorders
Just like any part of the body, maintaining the health of the prostate is crucial. Regular screenings and healthy lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in early detection and prevention of prostate disorders.
One of the primary concerns for men is Prostate Cancer. This occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate start to multiply out of control. It is the second most common cancer among men worldwide. Some prostate cancers grow slowly and need minimal or no treatment, while others are aggressive and can spread quickly.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is another common prostate disorder. This is not a cancer but a condition where the prostate gland becomes enlarged. This enlargement, common in older men, can squeeze the urethra and cause problems with urination.
Prostatitis is another frequent issue, involving the inflammation or infection of the gland. This leads to painful urination or ejaculation and lower back pain.
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis is a rare, severe form of Prostatitis caused by a bacterial infection. It comes with flu-like symptoms and, if diagnosed, requires immediate medical attention.
Being Proactive with Prostate Health
Given the potential complications associated with Prostate Cancer, it’s essential for men – especially those over 50 or with a family history of the disease – to undergo regular screenings. These screenings play a vital role in detecting the disease at a stage where treatment might have the most positive outcome. Commonly employed tests include the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test and the Digital Rectal Examination.
Bear in mind that a healthy lifestyle greatly benefits prostate health. Dietary habits, such as consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and heart-healthy food while minimizing fat intake, can result in a more robust prostate and overall improved health.
Never underestimate the power of regular physical exercise. Being active aids in maintaining an optimal weight, which is critical for a healthy prostate. Men who engage in consistent physical activity demonstrate lower chances of developing prostate problems than their inactive counterparts. Regular exercise cuts down the risk of BPH and Prostate Cancer as well.

Common Prostate Disorders
Recognizing Prostatitis: Inflammation of the Prostate
Prostatitis, a prevalent condition among men, refers to the inflammation of the prostate–a small, walnut-sized gland that secretes seminal fluid. This condition can stem from a bacterial infection, though in many cases, its cause remains unknown. Symptoms can range from groin pain and frequent urge to urinate to difficulty in urinating. In more severe cases, it may cause fever and present symptoms resembling the flu. In a chronic scenario–defined by symptoms lasting for at least three months–men may experience painful ejaculation and issues with sexual functions. If left unattended, chronic prostatitis can eventually lead to other conditions like chronic pelvic pain syndrome and could even affect fertility.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Enlargement of the Prostate
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), also known as prostate gland enlargement, is a common condition as men get older. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, and as it enlarges, it can put pressure on the urethra and interfere with the flow of urine. This can lead to symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, weak urinary stream, and the sensation of incomplete bladder emptying. More serious implications of untreated BPH include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, bladder damage, and kidney damage due to the high pressure within the urinary system caused by obstructive urinary flow.
Prostate Cancer: A Major Health Issue
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men. It grows slowly and is initially confined to the prostate gland, where it may not cause serious harm. However, while some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal treatment, others are aggressive and can spread quickly. Symptoms of prostate cancer can include difficulty urinating, blood in semen, discomfort in the pelvic area, bone pain or erectile dysfunction. If left untreated, prostate cancer can spread to bones or lymph nodes, leading to severe pain and significantly impacting life expectancy. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, which underscores the importance of regular prostate screening.
Hinting Towards Commonalities: The Importance of Regular Check-Ups
All these conditions underscore the importance for men, particularly as they age, to have regular check-ups that include prostate health. While the symptoms can have other causes, experiencing any unusual urinary symptoms or discomfort in the pelvic area should warrant a visit to a health care provider. Speaking openly about these symptoms with a doctor is a critical first step in early detection and effective treatment. Therapies for these prostate issues can range from medications and lifestyle changes to surgical interventions, with the choice dependent on the specific issue, its severity and the overall health and preferences of the individual.
Enhancing Prostate Health Through Screening and Awareness
Prostate health significantly influences overall wellbeing, which is why regular screenings such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests and digital rectal exams are critical for early disorder detection and intervention. Furthermore, patients need to stay informed and vigilant about maintaining prostate health. Recognizing one’s physiological signals, being alert about the early signs of common prostate disorders, and consulting a healthcare professional as necessary are areas that can markedly augment health prognosis. Open discourse and continuous education regarding prostate health empower men to take the helm in safeguarding their health.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Disorders
Acquainting Yourself with Prostate Disorders
The prostate is a small gland resembling a walnut found in men, responsible for the production of seminal fluid. With the increasing age, especially after 50, men are more likely to encounter disorders associated with this gland. The three most commonly seen prostate disorders include prostatitis- an inflammation or infection of the prostate, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) – a noncancerous enlargement, and prostate cancer.
Diagnostic Tests for Prostate Disorders
A number of diagnostic tests help physicians identify disorders of the prostate. The Digital Rectal Exam (DRE) is one of the most commonly used methods for detecting prostate anomalies. In a DRE, the doctor inserts a finger into the rectum to check the size of the prostate and to feel for any bumps or hard areas that might indicate a problem.
Another commonly used test is the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) testing. PSA is a protein produced by the prostate, and the levels of PSA in the blood can indicate abnormalities such as inflammation, enlargement, or cancer in the prostate.
If a DRE or PSA test indicates a potential problem, a biopsy may be undertaken. A biopsy involves sampling prostate tissue via a minimally invasive procedure so the cells can be examined under a microscope.
Imaging tests like ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can also be employed to visualize the prostate. These diagnostic tools can provide crucial insights into the size and structure of the prostate, helping to identify any abnormalities.
Understanding and Addressing Prostate Disorders
When dealing with prostate disorders, treatments are set based on the specific disorder and its severity. For instance, prostatitis normally necessitates antibiotics to combat the infection, and at times, pain relievers can be used to mitigate discomfort.
Treatment for BPH, or an enlarged prostate, could involve the use of medication aimed to relax the prostate muscles, making it easier to urinate. For severe cases, surgical intervention may be implemented to remove a portion of the prostate.
In many cases, patients with early-stage prostate cancer are placed under active surveillance, which involves regular monitoring using PSA testing, MRIs, and biopsies. As for more advanced prostate cancer, treatments can range from surgery to radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy.
Also of note are the advancements in prostate cancer treatments, where methods such as high-intensity focused ultrasound and cryotherapy are being examined. Additionally, immunotherapy, a type of treatment that utilizes the body’s own immune system to fight cancer, is under active research.
Choosing the most appropriate treatment isn’t a one-size-fits-all decision. It depends on numerous factors like the patient’s age, health condition, the specific disorder characteristics, and even personal preferences. Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is paramount as they can guide patients through the decision-making process regarding treatments for prostate disorders.

Preventive Measures and Prostate Health Maintenance
Early Detection For Better Prostate Health
Maintaining prostate health is of utmost importance for all men, with those above the age of 50 being particularly susceptible. Regular screenings play a vital role in early detection, significantly improving the effectiveness of treatment options and, consequently, the overall prognosis. The main screening tests available are the digital rectal exam (DRE) and the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. It’s important for men to have informed discussions with their healthcare provider concerning these tests and the frequency at which they should be conducted. Factors like age, family medical history, and racial or ethnic background can influence the necessity and regularity of these screenings.
Prostate Disorders: Staying Informed on Key Symptoms
The primary disorders that can affect prostate health are prostate cancer, enlarged prostate, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and prostatitis. Symptoms associated with these disorders can include frequent urination, difficulty in starting and stopping urination, blood in the urine, painful urination, and lower back pain. If these symptoms present, it is crucial to contact a healthcare provider to investigate further.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes for Prostate Health
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is imperative for overall prostate health. Regular exercise, such as strength and aerobic training, can reduce the risk of developing prostate disorders. Additionally, maintaining a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains and low in saturated fats, sugars, and processed foods can contribute to overall health and reduced risk for prostate disorders. Specifically, foods rich in lycopene, like tomatoes and watermelon, and foods with omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and nuts, have been linked to a reduction in prostate cancer risk.
Healthy Body Weight and Prostate Health
Maintaining a healthy body weight can also go a long way towards preserving prostate health. Obesity increases the risk of developing many health issues, including prostate cancer. Regular physical activity and a balanced diet can help manage body weight and reduce this risk.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also lead to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Therefore, individuals seeking to improve prostate health should look to limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding tobacco use.
Finally, it’s crucial to remember that while these strategies can reduce the risk of developing prostate disorders, they do not eliminate it entirely. Regular consultation with healthcare providers, routine screenings, and early detection remain the most effective ways to manage prostate health.
Taking good care of your prostate requires a blend of proactive preventive measures, lifestyle changes, regular screening, and timely medical intervention when needed. Despite the challenges that prostate disorders present, they are manageable with proper information, the right course of treatment, and collaborative care. Therefore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, observing dietary recommendations, and regular check-ups are essential steps that influence the journey towards comprehensive prostate health. The combination of these measures plays a significant part in early detection and efficient management of any potential prostate disorder, enhancing the scope for successful outcomes.
